Source - Storage I/O Control Technical Overview and Considerations for Deployment - Technical White paper
What is SIOC?
Storage I/O Control (SIOC) provides storage I/O performance isolation for virtual machines, thus enabling VMware® vSphere™ (“vSphere”) administrators to comfortably run important workloads in a highly consolidated virtualized storage environment. It protects all virtual machines from undue negative performance impact due to misbehaving I/O-heavy virtual machines, often known as the “noisy neighbour” problem. Furthermore, the service level of critical virtual machines can be protected by SIOC by giving them preferential I/O resource allocation during periods of congestion. SIOC achieves these benefits by extending the constructs of shares and limits, used extensively for CPU and memory, to manage the allocation of storage I/O resources. SIOC improves upon the previous host-level I/O scheduler by detecting and responding to congestion occurring at the array, and enforcing share-based allocation of I/O resources across all virtual machines and hosts accessing a datastore.
With SIOC, vSphere administrators can mitigate the performance loss of critical workloads due to high congestion and storage latency during peak load periods. The use of SIOC will produce better and more predictable performance behavior for workloads during periods of congestion. Benefits of leveraging SIOC:
• Provides performance protection by enforcing proportional fairness of access to shared storage
• Detects and manages bottlenecks at the array
• Maximizes your storage investments by enabling higher levels of virtual-machine consolidation across your shared datastores
How Storage I/O Control Works?
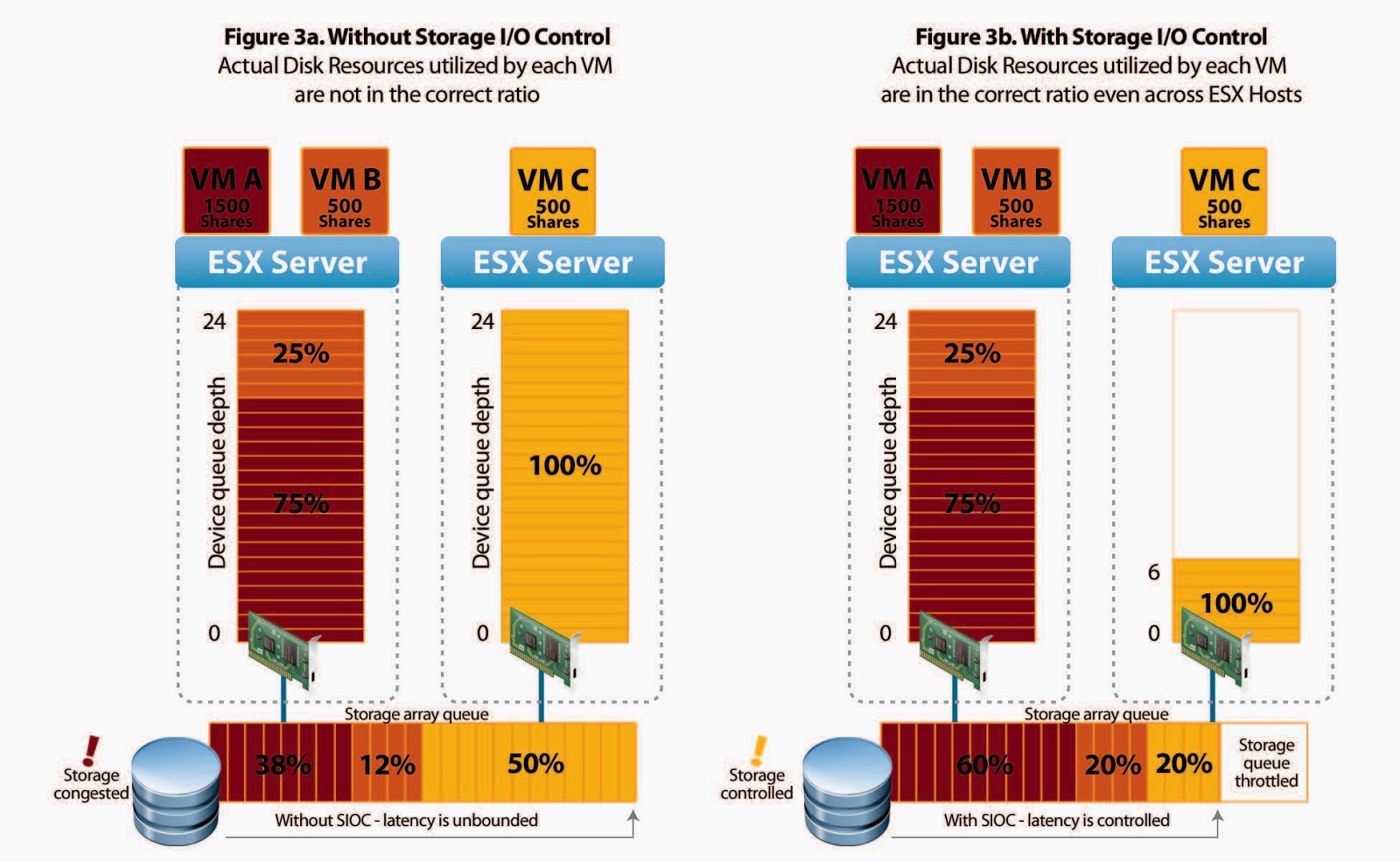
SIOC monitors the latency of I/Os to datastores at each ESX host sharing that device. When the average normalized datastore latency exceeds a set threshold (30ms by default), the datastore is considered to be congested, and SIOC kicks in to distribute the available storage resources to virtual machines in proportion to their shares. This is to ensure that low-priority workloads do not monopolize or reduce I/O bandwidth for high-priority workloads. SIOC accomplishes this by throttling back the storage access of the low-priority virtual machines by reducing the number of I/O queue slots available to them. Depending on the mix of virtual machines running on each ESX server and the relative I/O shares they have, SIOC may need to reduce the number of device queue slots that are available on a given ESX server.
Where it can be used?
SIOC can be used on any FC, iSCSI, or locally attached block storage device that is supported with vSphere 4.1. Review the vSphere 4.1 Hardware Compatibility List (http://www.vmware.com/go/hcl) for the entire list of supported storage devices. SIOC is supported with FC and iSCSI storage devices that have automated tiered storage capabilities.
Any Limitations?
Yes.
What is SIOC?
Storage I/O Control (SIOC) provides storage I/O performance isolation for virtual machines, thus enabling VMware® vSphere™ (“vSphere”) administrators to comfortably run important workloads in a highly consolidated virtualized storage environment. It protects all virtual machines from undue negative performance impact due to misbehaving I/O-heavy virtual machines, often known as the “noisy neighbour” problem. Furthermore, the service level of critical virtual machines can be protected by SIOC by giving them preferential I/O resource allocation during periods of congestion. SIOC achieves these benefits by extending the constructs of shares and limits, used extensively for CPU and memory, to manage the allocation of storage I/O resources. SIOC improves upon the previous host-level I/O scheduler by detecting and responding to congestion occurring at the array, and enforcing share-based allocation of I/O resources across all virtual machines and hosts accessing a datastore.
With SIOC, vSphere administrators can mitigate the performance loss of critical workloads due to high congestion and storage latency during peak load periods. The use of SIOC will produce better and more predictable performance behavior for workloads during periods of congestion. Benefits of leveraging SIOC:
• Provides performance protection by enforcing proportional fairness of access to shared storage
• Detects and manages bottlenecks at the array
• Maximizes your storage investments by enabling higher levels of virtual-machine consolidation across your shared datastores
How Storage I/O Control Works?
SIOC monitors the latency of I/Os to datastores at each ESX host sharing that device. When the average normalized datastore latency exceeds a set threshold (30ms by default), the datastore is considered to be congested, and SIOC kicks in to distribute the available storage resources to virtual machines in proportion to their shares. This is to ensure that low-priority workloads do not monopolize or reduce I/O bandwidth for high-priority workloads. SIOC accomplishes this by throttling back the storage access of the low-priority virtual machines by reducing the number of I/O queue slots available to them. Depending on the mix of virtual machines running on each ESX server and the relative I/O shares they have, SIOC may need to reduce the number of device queue slots that are available on a given ESX server.
Where it can be used?
SIOC can be used on any FC, iSCSI, or locally attached block storage device that is supported with vSphere 4.1. Review the vSphere 4.1 Hardware Compatibility List (http://www.vmware.com/go/hcl) for the entire list of supported storage devices. SIOC is supported with FC and iSCSI storage devices that have automated tiered storage capabilities.
Any Limitations?
Yes.
- However, when using SIOC with automated tiered storage, the SIOC Congestion Threshold must be set appropriately to make sure the storage device’s automated tiered storage capabilities are not impacted by SIOC.
- At this time, SIOC is not supported with NFS storage devices or with Raw Device Mapping (RDM) virtual disks. SIOC is also not supported with datastores that have multiple extents or are being managed by multiple vCenter Management Servers.
- SIOC requires Single-extent datastores only.

No comments:
Post a Comment